Git repositories (/git)
The /git endpoint is dedicated to export/import modules using Git over HTTP(S).
This feature relies on the Eclipse JGit library.
In production this Git endpoint's URL should be restricted only to allowed origins e.g. using URL filtering on request's origin IP address or similar approaches.
Configuration
The Git repositories are stored on the server file system.
Due to the way the JGit library is designed, the base folder in which these repositories will be located must be passed to the application server as a system property.
This can be done either:
- by passing a JVM argument
-Dgit.basedir=<path>when starting the application server - by setting it in the
application.propertiesfile of your application
Then you also need to set the USE_GIT system parameter to yes.
Export
To export the MyModule module as a Git repository the first thing to do is to create or update the module's repository
using the dedicated action on the Module object:
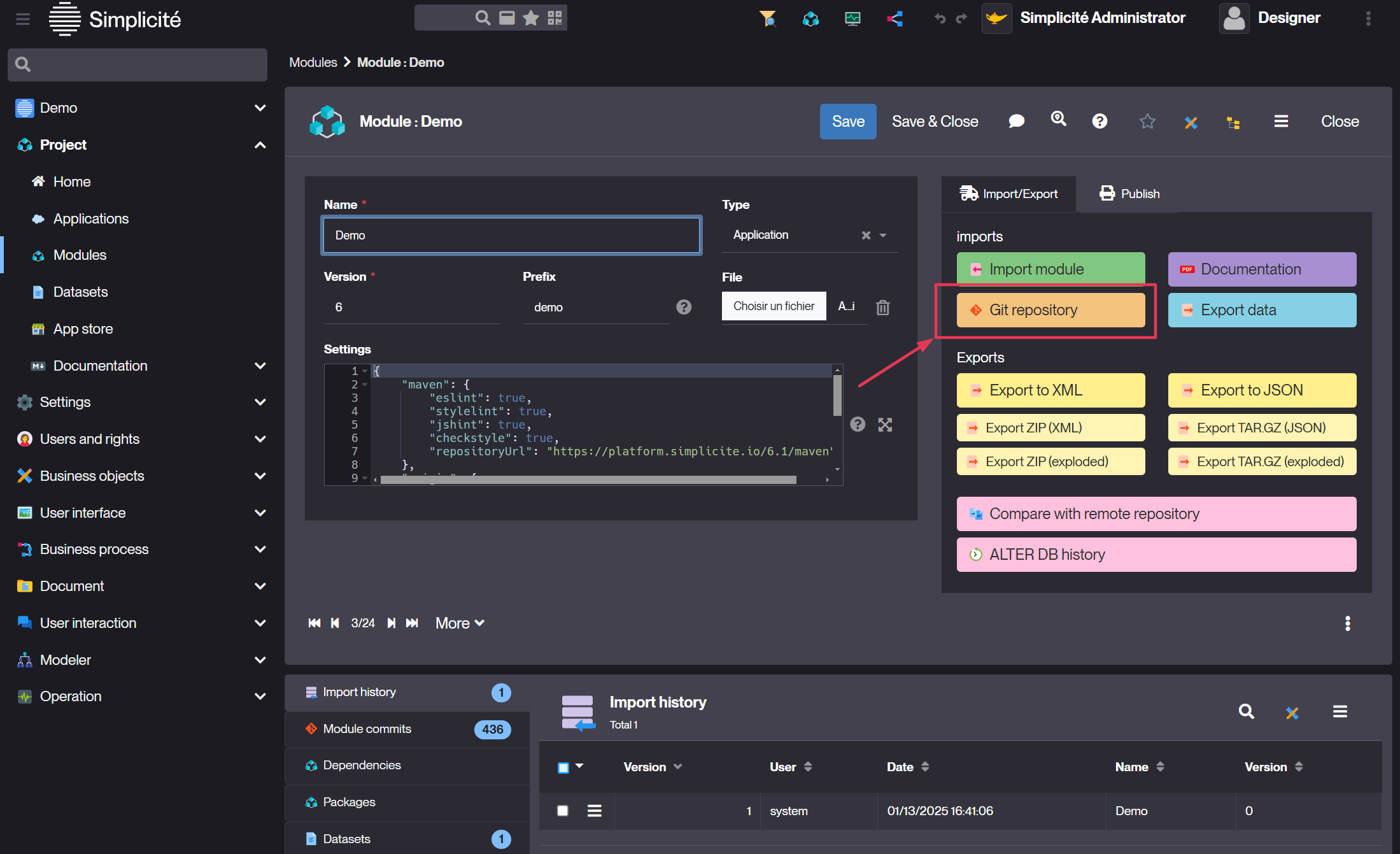
Then you can clone the module's repository by:
git clone http(s)://<host name>[/<app context root>]/git/<module name>
The credentials you have to use in this case are the same as the one you can use for the I/O interface.
Import
Any git push [origin] on the cloned module's repository triggers a module import
(e.g. after having made some local changes or to upgrade another instance by pushing on another remote).
Import from an origin remote
It is possible to configure a module that is linked to an external Git repository by adding following settings to your module:
E.g. from another instance's module repository:
{
"type": "git",
"origin": {
"uri": "http(s)://<instance host name>[/<instance app context root>]/git/<module name>",
"username": "<I/O user's login>",
"password": "<I/O user's password>"
}
}
Any call to the Import module action will then result in either a clone or a pull on the configured remote Git repository.
Typical use case is to link a "secondary" instance to a "primary" instance. In such a case there are 2 possible ways to export/import a module from the "primary" to the "secondary" instance:
- Directly use the Import module action from the "secondary" instance (that will be pulling last commit(s) from the "primary" instance)
- Use a clone of the "primary" instance Git repository configured with an additional remote that points to the "secondary" instance.
Then
git pullwill pull from the "primary" instance andgit push <remote name>will push to the "secondary" instance.
E.g. from a public GitHub repository:
{
"type": "git",
"origin": {
"uri": "https://github.com/<profile>/<repository>.git"
}
}
If you plan to push on this public GitHub repository you must add a username and password.
As of version 5.2, you can set the JVM properties (remote.git.username/password) or the environment variables (REMOTE_GIT_USERNAME/PASSWORD)
if you want to avoid configuring username/password credentials in your module's settings.
A much better approach being to use a SSH URI with configured SSH public/private keys.
Advanced
The Git repositories created/cloned by Simplicité:
- Are non bare repositories, the local work tree is needed by the export/import processes
- Have the following configuration set by default in
.git/configfile to allow read-write access over HTTP(S):
[http]
uploadpack = true
receivepack = true
If you manually create/clone repositories used by Simplicité (which is not supposed to be done except for very specific needs) make sure to create/clone non bare repositories and make sure to have these two options activated (which is not the case by default).
Branches
You can specify the branch to use in the origin definition (or in the remotes definitions, see bellow):
{
"type": "git",
"origin": {
(...)
},
"branch": "<branch, defaults to 'master'>"
}
Other remotes
You can specify additional remotes:
{
"type": "git",
"origin": {
(...)
}
"remotes": {
"remote1": {
(...)
},
(...)
"remoteN": {
(...)
},
}
}
Each remote definition use the same syntax as the origin definition.
Maven settings
If required, you can specify additional settings to change the Maven settings generated in the pom.xml.
{
"maven": {
"name": "<alternative name>",
"description": "<alternative description>",
"javaVersion": "<alternative Java version>",
"url": "<alternative instance URL>",
"repositoryUrl": "<alternative Maven repository URL>",
"checkstyle": <true to execute the CheckStyle verification at build>,
"jshint": <true to execute the JSHint check at build>,
"eslint": <true to execute the ESLint check at build>,
"stylelint": <true to execute the StyleLint check at build>,
"dependencies": [
{
"groupId": "<additional dependency's group ID>",
"artifactId": "<additional dependency's artifact ID>",
"version": "<additional dependency's version>"
},
(...)
]
}
}
SonarQube settings
If required, you can specify additional settings to change the SonarQube® configuration generated in the pom.xml.
{
"sonar": {
"projectKey": "<alternative project key>",
"projectName": "<alternative project name>",
"projectVersion": "<alternative project version>",
"<custom name>": "<additional custom setting, will be prefixed by 'sonar.'>"
}
}
Linting settings
Checkstyle
If required, you can specify additional settings to change the Checkstyle® configuration generated in the pom.xml.
{
"checkstyleConfig": "<default|google|<XML resource name>>",
"checkstyleReportFile": "<report file>"
}
JSHint
If required, you can specify additional settings to change the JSHint® configuration.
{
"jshintConfig": "<default|<JSON resource name>>"
}
ESLint
If required, you can specify additional settings to change the ESLint® configuration.
{
"eslintConfig": "<default|<JavaScript resource name>>"
}
StyleLint
If required, you can specify additional settings to change the StyleLint® configuration.
{
"stylelintConfig": "<default|<JSON resource name>>"
}
GPG signature
As of version 5.3 it is possible to enable GPG signature of commits.
This uses the GIT_GPG_SIGNATURE_KEYID system parameter which denotes the GPG key ID to use for signature.
This system parameter can be overridden on a per-user base.