Databases
MySQL 5.x / MariaDB
JDBC driver
With MySQL version 5.x / MariaDB, you must use a 5.x JDBC Driver.
Connecting over SSL
Some MySQL 5.x / MariaDB servers must be accessed over SSL, in such a case some additional arguments are needed:
Connecting from the command line:
mysql --protocol=tcp --ssl-mode=REQUIRED --host=<host> --port=<port> --database=<database> --user=<username> --password=<password> [--default-character-set=utf8]
JDBC URL:
jdbc:mysql://<username>:<password>@<host>:<port>/<database>?autoReconnect=true&verifyServerCertificate=false&useSSL=true&requireSSL=true[&useUnicode=yes&characterEncoding=utf8&characterResultSets=utf8]
Maximum packet size
You need to check and increase if needed the max_allowed_packet settings to be compliant with your requirement, a good minimal value is 16M.
If you are using BLOBs for files you should set it accordingly to the maximum size of files you are supposed to handle.
Limitations
MySQL 5.x / MariaDB have a limit of 64Kb per records (except LOBs columns)
MySQL 8.x
JDBC driver
With MySQL version 8.x, you must use a 8.x JDBC Driver.
Datasource configuration
You will have to alter your META-INF/context.xml manually to use the new driver class com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver (instead of the deprecated com.mysql.jdbc.Driver)
You will also need to add an explicit time zone to your database JDBC URL, e.g. &serverTimezone=Europe/Paris
PostgreSQL
Backslashes
Beware backslashes treatment in PostgreSQL :
Before PostgreSQL 9.1, the configuration variable standard_conforming_strings was turned off by default.
That's why PostgreSQL did not treat backslashes literally but interpreted them.
But according to SQL standard, backslashes should be treated literally. So, from PostgreSQL 9.1,
the standard_conforming_strings config variable has been turned on.
If you want your code be portable between different database engines, you may want to have this config variable turned on. So if you're on PostgreSQL 9.0 or lower :
alter database YOUR_DB set standard_conforming_strings=on;
An other means is to use the E PostgreSQL specific prefix to construct a literal query regardless server or connection configuration like standard_conforming_strings.
Example :
set standard_conforming_strings to true;
select 'hop\'';
hop\'
select E'hop\'';
hop'
set standard_conforming_strings to false;
select 'hop\'';
hop'
select E'hop\'';
hop'
Case sensitive search
By default PostgreSQL does not provide case-insensitive search match when using standard LIKE comparator.
Active maintenance releases of Simplicité now use by default the non standard ILIKE comporator.
See this document for details.
Database linking
PostgreSQL 9.6+'s extension module postgres_fdw allows you to link a remote database into a local database.
To do so, connect to the local database as the postgres super administrator:
sudo su - postgres -c "psql -d <local database name>"
Then issue the following commands:
CREATE EXTENSION postgres_fdw;
CREATE SERVER <arbitrary remote server name> FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER postgres_fdw OPTIONS (host '<remote host name or IP>', port '<remote port>', dbname '<remote database name>');
CREATE USER MAPPING FOR CURRENT_USER SERVER <arbitrary remote server name> OPTIONS (user '<remote username>', password '<remove password>');
CREATE USER MAPPING FOR <local username> SERVER <arbitrary remote server name> OPTIONS (user '<remote username>', password '<remove password>');
CREATE SCHEMA <arbitrary local schema name>;
IMPORT FOREIGN SCHEMA <remote schema name, e.g. public> FROM SERVER <arbitrary local server name> INTO <arbitrary local schema name>;
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA <arbitrary local schema name> TO <local username>;
GRANT <ALL PRIVILEGES|SELECT> ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA <arbitrary local schema name> TO <local username>;
Use ALL PRIVILEGES for read+write access, SELECT for read-ony access.
Then after connecting as local user to local database:
PGPASSWORD=<local password> psql -h <local host> -p <local port> -U <local username> -d <local database>
you can access remote tables like this select * from <arbitrary local schema name>.<remote table name>;
You can only import some of the remote schema's tables by appending LIMIT (<remote table name 1>, <remote table name 2>, ...)
to the above IMPORT FOREIGN SCHEMA statement. Of course you can use other linking strategies depending on your requirement.
Oracle
Limitations
- Varchars are limited to 4000, over 4000 Simplicité generates CLOBs columns (that are, thus, not indexable)
- Tables, aliases and columns names are limited to 30 characters
Oracle XE (express) 18c server installation
All following activities must be done as root.
Installation and configuration
Download the RPMs from Oracle XE download site
oracle-database-preinstall-18c-1.0-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
oracle-database-xe-18c-1.0-1.x86_64.rpm
Install them:
yum -y localinstall oracle-database*
Then setup the server (this includes setting the <system password> used below):
/etc/init.d/oracle-xe-18c configure
Enable the service:
systemctl enable oracle-xe-18c
And start it (if not already started by setup):
systemctl start oracle-xe-18c
Post-installation
Create environment file:
cat << EOF > /etc/profile.d/oraclexe.sh
ORACLE_HOME=/opt/oracle/product/18c/dbhomeXE
export ORACLE_HOME
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${ORACLE_HOME}/lib:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH
SQLPATH=${ORACLE_HOME}/lib:${SQLPATH}
export SQLPATH
PATH=${ORACLE_HOME}/bin:${PATH}
export PATH
NLS_LANG=AMERICAN_AMERICA.UTF8
export NLS_LANG
ORACLE_SID=XE
export ORACLE_SID
EOF
chmod +x /etc/profile.d/oraclexe.sh
Then you can connect as SYSDBA either using the oracle account (no password needed in this case):
sudo su - oracle
sqlplus / as sysdba
or from any other account:
sqlplus system/<system password>@XE as sysdba
Check your default charset against the NLS_LANG:
sql> select value from nls_database_parameters where parameter='NLS_CHARACTERSET'
And adapt the NLS_LANG value:
NLS_LANG=AMERICAN_AMERICA.ALL32UTF8
export NLS_LANG
On windows to load an SQL script encoded in UTF8 through the cmd prompt, you will have to change the default Windows code page (850) first:
chcp 65001
set NLS_LANG=.AL32UTF8
sqlplus <user>/<pwd>
sql> @script.sql
Optimization
APEX is a management web UI that is managed by the Oracle server. As it requires lots of resources, it is better to disable it if not needed.
To do so, set APEX port to zero:
EXEC DBMS_XDB.SETHTTPPORT(0);
COMMIT;
To reactivate it if needed, reset APEX port to any non zero value (e.g. 8080):
EXEC DBMS_XDB.SETHTTPPORT(8080);
COMMIT;
Warning about express JDBC driver
Some of the versions of the Oracle express JDBC driver may cause some performance issues in high data volume contexts.
You should use an up-to-date regular version of the Oracle JDBC driver instead.
Oracle 12c instant client installation
This applies only when you only need an Oracle client on your machine.
Installation
Download the 3 instant client PRM packages from Oracle website:
- basic
- sqlplus
- tools
And install them:
rpm -ivh oracle-instantclient12.2-basic-12.2.0.1.0-1.x86_64.rpm oracle-instantclient12.2-sqlplus-12.2.0.1.0-1.x86_64.rpm oracle-instantclient12.2-tools-12.2.0.1.0-1.x86_64.rpm
Post-installation
Create environment file:
sudo vi /etc/profile.d/oracleclient.sh
sudo chmod +x /etc/profile.d/oracleclient.sh
With following content:
ORACLE_HOME=/usr/lib/oracle/12.2/client64
export ORACLE_HOME
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${ORACLE_HOME}/lib:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH
PATH=${ORACLE_HOME}/bin:${PATH}
export PATH
NLS_LANG=AMERICAN_AMERICA.UTF8
export NLS_LANG
You can improve sqlplus behavior by appending options in $ORACLE_HOME/sqlplus/admin/glogin.sql like:
set pagesize 999
set linesize 999
Microsoft SQLServer
Installation
The up-to-date instructions are in this document:
Install the YUM repository:
sudo curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/mssql-server.repo https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/7/mssql-server-preview.repo
Install server:
sudo yum install mssql-server
Enable and start server:
sudo systemctl enable mssql-server
sudo systemctl start mssql-server
Limitations
Cumulated length of indexed columns cannot exceed 900 bytes (this makes any long text field non indexable)
Physical model
Meta-model schema
The default database contains all tables needed by the runtime. System tables are prefixed by:
m_for the core system (objects, fields, rights...)bpm_for business process and orchestrationsocial_for all social features- etc.
They must be accessed through the UI or API to be updated.
Some important tables:
m_system: contains global platform settingsm_userandm_resp: contains users and responsibilitiesm_document: contains all the documents attached to document fields- This table will be huge when
DOC_DIR=BLOB(see below) - Otherwise the table only contains the path to the
dbdocdirectory
- This table will be huge when
m_log: contains all persistent application log events and metricsm_session: contains all sessions
Generated schema
Each module import will generate automatically its related schema:
- all tables and columns based on Business object definitions
- common indexes per business object/table:
- the unique primary key (the
row_idif not overridden) - one unique user-key based on ordered functional-key fields: syntax
<table>_<column>_uk - non unique indexes on textual searchable fields: syntax
<table>_<column>_idx
- the unique primary key (the
- foreign-keys per link:
- non unique index on foreign-keys: syntax
<table>_<column>_fk - integrity constraint on foreign-keys: syntax
<table>_<column>_fkc - non unique index on meta-object fields (logical link to
<object>:<id>): syntax<table>_<column>_mo
- non unique index on foreign-keys: syntax
Example of Demo's physical data model:
The generated indexes are enough to optimize the SQL queries generated by the engine (UI searches, inner/outer joins...). Designer can add other indexes to optimize certain complex/specific queries:
- with a shared code (type SQL) in the application module
- to be applied on each instance (with the shared code
Applyaction on UI, or the DB access, or with a CLI sql)
Business model upgrade
The engine generates the ALTER of tables and columns when the name/type/length are updated during a module (re)import.
It replaces also the indexes and foreign-keys:
- The queries can be in error due to DB limitation or incoherent data, for examples:
- altering a varchar column to date or integer is forbidden
- or the data contains mismatching data
- the new User-Key is non unique with existing records in table
- the index is limited to a certain size...
- The designer must analyze the logs after installation to fix the DB/data errors before re-ALTERing.
- Or may contact the support for unsolvable problem or ask for advice.
The engine never DROPs a table or a column even if the business object/field is deleted:
- For rollback reasons in case of error
- After a successful migration, the designer/DBA have to drop the deprecated table/column
The platform can not migrate the data automatically in case of complex model refactoring. Designer have to build and apply SQL patches to update data, for examples:
- changing a column to more complex type (ex: deprecated column varchar to a new date column)
- changing a 0,N relationship to a N,N table: all references have to be moved/inserted in the N,N
- splitting one big object/table in several objects/tables...
DB Performances
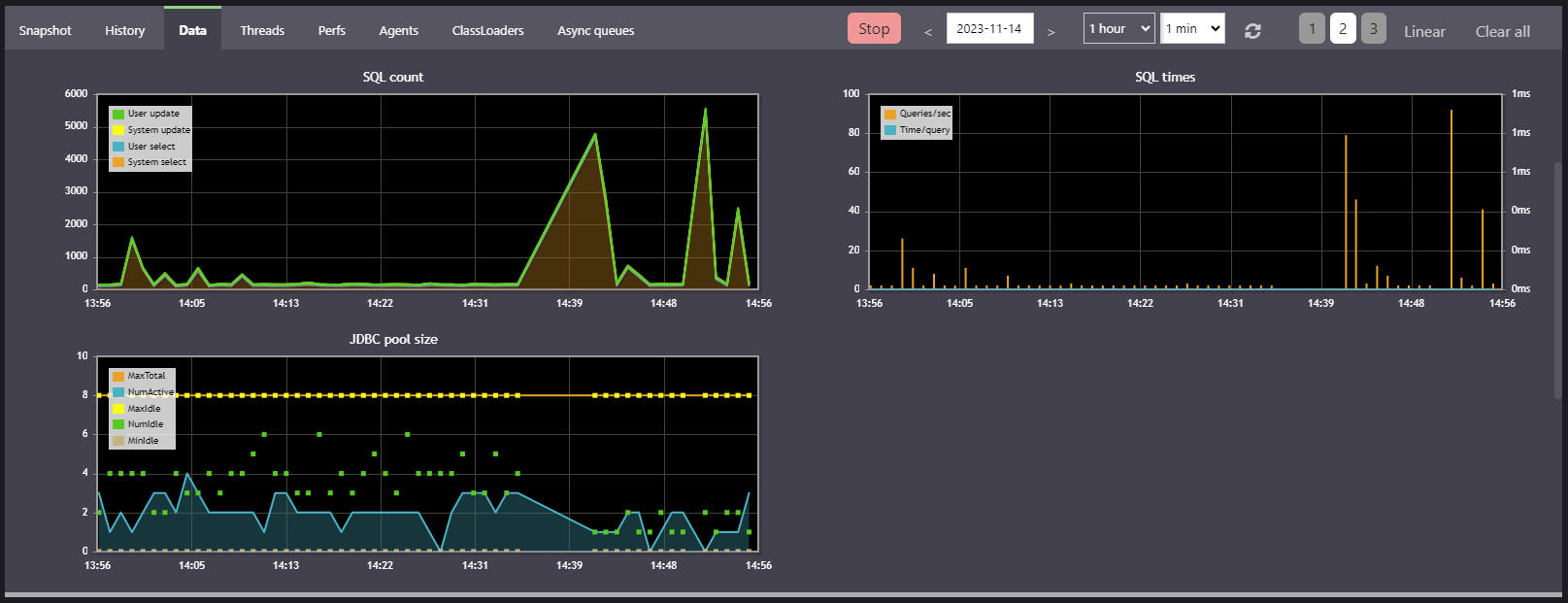
To analyze the DB performances and the long queries, you can use the Operation/Monitoring/Data tab.
It offers 3 charts to monitor and detect common saturations:
SQL count: counts the queriesselectandupdatein timeSQL times: tracks the fluidity of access, queries/second and time/query in timeJDBC pool size: monitors the connections pool to the database in time
The monitoring keeps in mind the top 10 long-queries:
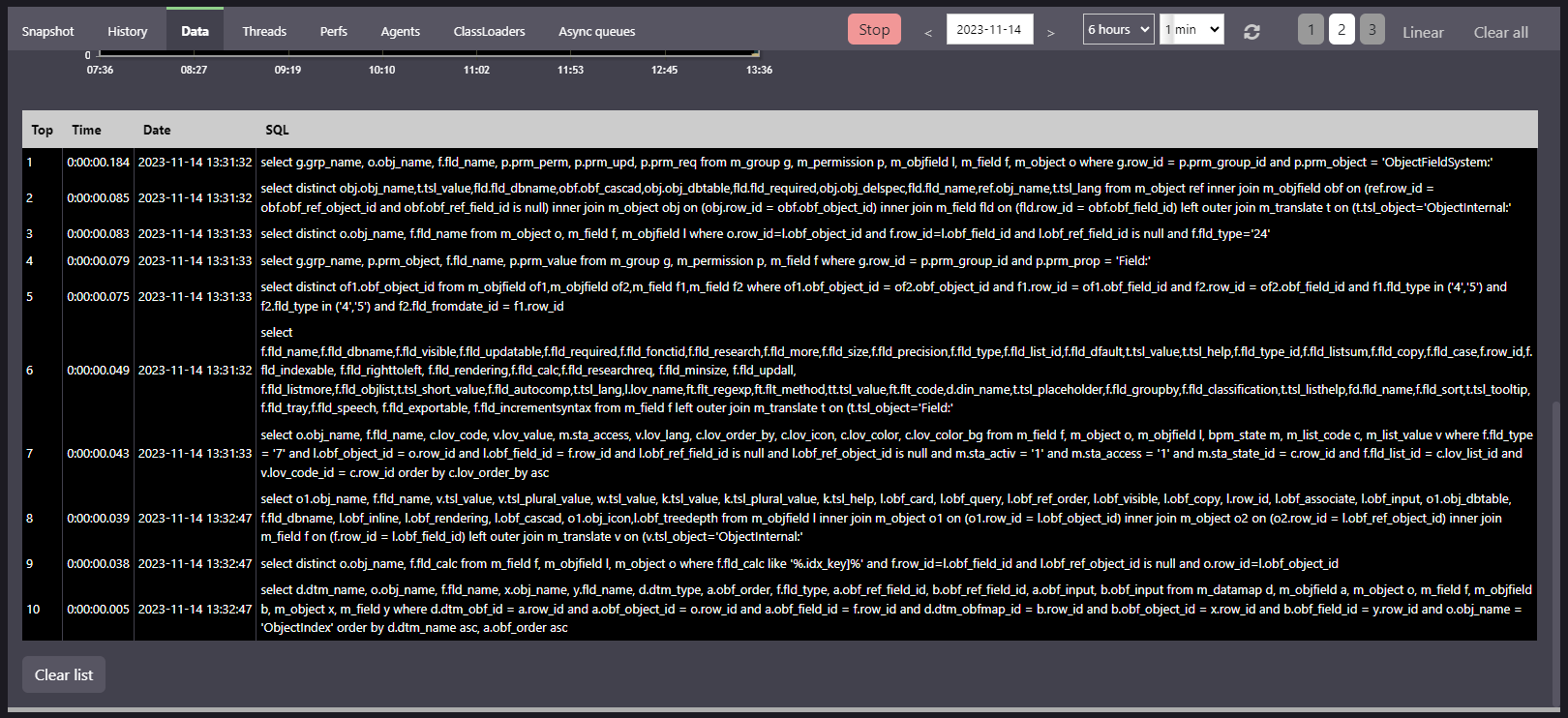
When the duration is too long the query has to be analyzed with an external CLI to EXPLAIN PLAN:
- Some internal queries can be numerous or long but called once to load meta-data during a clear-cache (full-scan of models).
- For the others, indexes can be added has described above with a SQL shared script.
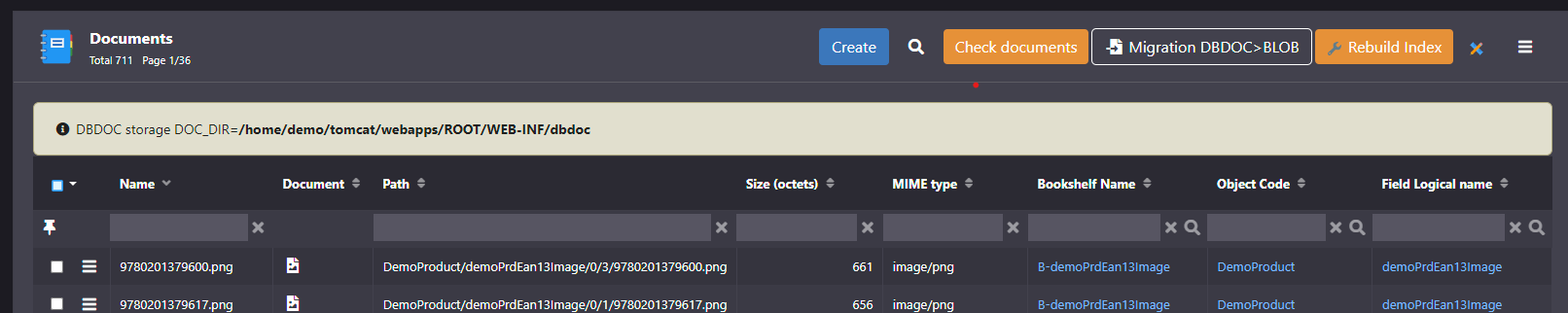
Documents storage and migration
The m_document table contains all files attached to document's fields.
It can store the documents in 2 ways through the system parameter DOC_DIR:
- Way BLOB in the database
DOC_DIR=BLOBDOC_LOCAL_DIR= path to fallback directory- Saving the database will also save all documents
- Way DBDOC in a local/mounted file system
DOC_DIR= the (relative) path to the documents directory- this external directory and the database must be backed-up at the same time to ensure data consistency.
Since V6, it is possible to migrate easily from/to BLOB using the UI actions.
Example to migrate the documents to BLOB:
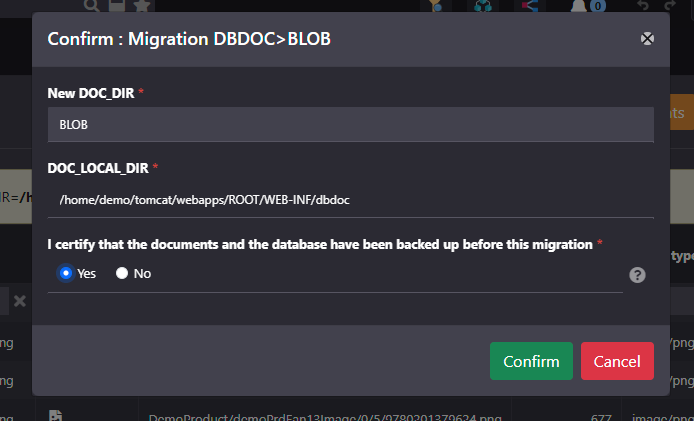
The migration is irreversible in case of error (not enough disk to write files, partition size of m_document...):
- It is imperative to first save the database and the documents for a possible rollback.
- It is a long async process running depending on the quantity of documents, a test may be done first on a copy of the production instance.
- It is strongly recommended to disable all UI/API access during the migration (if users use documents).
- It can be stopped/launched several times: each document is migrated once, the process restarts at the last migrated document.
- When all documents are migrated, the
DOC_DIRis updated to the final value.
