Simplicité; Instances Manager for CentOS
This document applies to the legacy Simplicité Instances Manager (SIM) software for CentOS 7 (this OS is not maintained anymore).
Introduction
Architecture
The SIM offers a command line interface (CLI), a web services interface (API), built on top of the CLI, and a web user interface (UI), built on top of the API, to manage several Simplicité instances on a server:
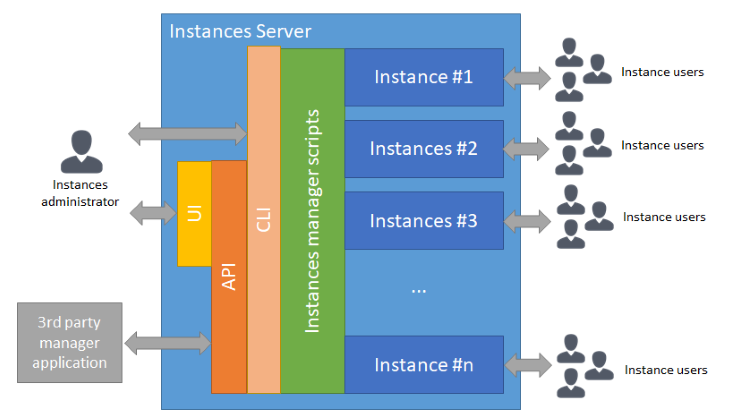
Using the CLI offers the full features of the SIM, the API and the UI offers only a subset of the CLI features.
Features
The SIM offers the following features:
- Get SIM configuration and statistics
- Upgrade SIM software
- List instances
- Add new instances
- Backup instances
- Rename instances
- Copy instances
- Upgrade instances
- Start instances
- Stop instances
- Reset instance
- Delete instances
- Get instances' configuration
- Get instances' health-check data
- Get instances'default I/O credentials
- Get instances' action history
- View or download instance logs
- Get instance access logs report
- Download instances' data
- Mark instance as protected
- Mark instance as automatically upgraded
- Mark instance as automatically backed up
- Process SonarQube analysis on instance's module
- Run unit tests on a instance
All above actions are triggered manually using the CLI, the API or thee UI.
The following actions are triggered by a system-level task scheduler (cron table);
- Automatic upgrade of instances marked as automatically upgraded
- Automatic backup of instances marked as automatically backed up
Note that the automatic backup can be configured to export the backup files to a remote storage. Otherwise the backup files are only stored locally on the SIM server.
Implementing pre/post action hooks (see bellow) allow you to customize the standard features of the SIM.
UI usage
The instances manager UI is available on <base URL>/ui.
The UI offers uses the API documented bellow and thus offers equivalent - but somehow limited by a simplified user experience - services.
To create a new instance, enter an instance name (or leave empty for an automatic name) then select the version from the Create button:
To manage an existing instance, click on one instance in the list, then select the action from the Action button:
The Monitor action opens a new tab and allow to monitor a given instance by tracking record of recurring health checks:
API usage
The instances manager API is available on <base URL>/api.
The API services are using HTTP GET methods only and URL-encoded parameters only. All API responses are JSON-encoded.
For all API services, you can get a pretty printed JSON response by appending &prettyprint=true.
By default the authentication method is HTTP basic auth (username + password), but client certificate authentication can also be used.
The examples bellow are using the curl command HTTP client, <credentials> is thus either:
-u <username>:<password>for username & password authentication method--cert-type pem --cert <path to your PEM client certificate file> --key <path to your PEM certificate key file>or--cert-type P12 --cert <path to your P12 client certificate file>[:'<your password>']for client certificate authentication method
Manager API
Get API configuration
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api[?action=config]
The action parameter can be omitted in this case as config is the default action.
Get available versions
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=versions
Instances API
List instances
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=list[¶m=<version>]
The parameters are:
param(optional) the version for filtering. If you don't provide an explicit value no version-based filtering is done.
Create instance
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=add[&name=<instance name>][¶m=<version (or instance name to clone)>][&options[<option name>]=<option value>]
The parameters are:
name(optional) the name of the instance to create, must be strictly alphanumerical and of length 3 to 20. If you don't provide an explicit name, a random name (10 alphanumerical characters) is generated and used.param(optional) the version of the instance (e.g. ``) or the name of an existing instance to clone (e.g.sft65drt7y). If you don't provide an explicit version, the configured default version is used.options[](optional) the options array for instance creation:options[database]overrides default database (hsqldb,mysql,postgresqldepends on which databases engine are available on the server)options[protected]overrides default protected flag (yesorno)options[auto_save]overrides default automatic save flag (yesorno)options[auto_update]overrides default automatic update flag (yesorno)
Stop instance
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=stop&name=<instance name>[&force=<true|false>]
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to stop.force(optional) use "force" stopping strategy (true) or standard strategy (false= default)
Start instance
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=start&name=<instance name>
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to start.
Instance health check
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=health&name=<instance name>
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to get health check for.
Instance I/O credentials
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=iocredentials&name=<instance name>
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to get I/O credentials from.
Instance last logs
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=logs&name=<instance name>
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to get logs for.
Download instance logs
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=download¶m=logs&name=<instance name>
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to download logs for.
Get access logs report
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=accesslogs&name=<instance name>
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to get access logs report for.
Upgrade instance
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=upgrade&name=<instance name>
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to upgrade.
Upgrade all automatic upgrade instances
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=upgradeall
Reset instance
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=reset&name=<instance name>
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to reset.
A reset will erase all existing configuration and data.
Delete instance
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=del&name=<instance name>[&force=<true|false>]
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to delete.force(optional) use "force" deletion strategy (true) or standard strategy (false= default)
Clone instance
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=clone&name=<instance name>¶m=<cloned instance name>
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to clone.param(required) the name of the cloned instance.
Rename instance
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=rename&name=<instance name>¶m=<new instance name>
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to rename.param(required) the new name of the instance.
Save instance on server
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=save&name=<instance name>
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to save.
Save all automatic save instances on server
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=saveall
Download instance data
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=download¶m=data&name=<instance name>
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to download data for.
Download instance webapp
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=download¶m=webapp&name=<instance name>
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to download webapp for.
Download full instance
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=download&name=<instance name>
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to download.
Once downloaded you can simply unzip the instance and launch it locally:
Windows:
@echo off
set JAVA_HOME=<path to your JDK home, e.g. %CD%\jdk-1.8.0>
set PATH=%JAVA_HOME%\bin;%PATH%
set TOMCAT_ROOT=<path to your instance, e.g. %CD%\tomcat>
set TOMCAT_ADMIN_PORT=8005
set TOMCAT_HTTP_PORT=8080
set TOMCAT_HTTPS_PORT=8443
set JAVA_OPTS=%JAVA_OPTS% -server -Dserver.vendor=tomcat -Dserver.version=9 -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -Dgit.basedir=%TOMCAT_ROOT%\webapps\ROOT\WEB-INF\git
set JAVA_OPTS=%JAVA_OPTS% -Dtomcat.adminport=%TOMCAT_ADMIN_PORT% -Dtomcat.httpport=%TOMCAT_HTTP_PORT% -Dtomcat.httpsport=%TOMCAT_HTTPS_PORT%
if not exist %TOMCAT_ROOT%\work mkdir %TOMCAT_ROOT%\work
if not exist %TOMCAT_ROOT%\temp mkdir %TOMCAT_ROOT%\temp
if not exist %TOMCAT_ROOT%\logs mkdir %TOMCAT_ROOT%\logs
cd %TOMCAT_ROOT%\bin
.\startup.bat
exit
Linux:
#!/bin/bash
export JAVA_HOME=<path to your JDK home, e.g. `pwd`/jdk-1.8.0>
export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
export TOMCAT_ROOT=<path to your instance, e.g. `pwd`/tomcat>
export TOMCAT_ADMIN_PORT=8005
export TOMCAT_HTTP_PORT=8080
export TOMCAT_HTTPS_PORT=8443
export JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -server -Dserver.vendor=tomcat -Dserver.version=9 -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -Dgit.basedir=$TOMCAT_ROOT/webapps/<instance|'ROOT'>/WEB-INF/git"
export JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Dtomcat.adminport=$TOMCAT_ADMIN_PORT -Dtomcat.httpport=$TOMCAT_HTTP_PORT -Dtomcat.httpsport=$TOMCAT_HTTPS_PORT"
[ ! -d $TOMCAT_ROOT/work ] && mkdir $TOMCAT_ROOT/work
[ ! -d $TOMCAT_ROOT/temp ] && mkdir $TOMCAT_ROOT/temp
[ ! -d $TOMCAT_ROOT/logs ] && mkdir $TOMCAT_ROOT/logs
cd $TOMCAT_ROOT/bin
./startup.sh
Instance actions history
curl -k -s <credentials> <base URL>/api?action=history&name=<instance name>
The parameters are:
name(required) the name of the instance to get action history for.
CLI usage
The sim CLI offers the following actions:
CLI actions
Usage
sim
or
sim --help
Get configuration
sim config
Get available versions
sim versions
Upgrade SIM and retrieve latest templates
sim refresh
On a standard SIM deployment, this is done automatically on a regular basis using a dedicated cron task (by default every day during the night).
List instances
sim list [<version|single keyword> or SQL:<sql where clause>]
Example of SQL where clause (i is the table alias for instances and v the table alias for versions):
sim list "SQL:i.version in ('4.0', '5') and i.status = 'started' and i.version_date < v.date"
List one single instance
sim get <name>
Add an instance
sim add <name> [<version> [<database>]]
If version is omitted the default version is used
If database is omitted the default database is used (note that if you want to specify a database you must specify the version)
Save an instance
sim save <name>
During the save action the Tomcat process, if running, is suspended to ensure saved data consistency.
Reset an instance
sim reset <name> <version>
A reset action will erase all existing configuration and business data.
Delete an instance
sim delete|rm <name>
Clone an instance
sim clone|cp <name to clone> <cloned name>
Rename an instance
sim rename|mv <name> <new name>
Stop/start an instance
sim stop <name>
sim start <name>
Upgrade an instance
sim upgrade|up <name>
View last logs of an instance
sim logs <name>
Download an instance
sim download <name> <type: all|webapp|data|logs>
Get access logs report for an instance
sim accesslogs <name>
Control the Tomcat server of an instance (only applicable on a started instance)
sim tomcat-<status|stop|start|debug> <name>
Using debug is similar to start except that the Tomcat server is then started in JPDA debug mode.
The JPDA port is available in the JPDA_ADDRESS environment variable.
This port is temporary allowed through the firewall.
Starting Tomcat in debug mode must only be done when required, it slows down your instance and makes it vulnerable. It is only suitable for punctual debugging.
Run ant task for an instance
sim ant-<task: purgelogs|purgejobs|purgesupervisions|purgerecyclebin|purgeexports|purgetempfiles|purgeall|buildindex|...> <name> [<param>]
Protect/unprotect an instance
sim protect <name>
sim unprotect <name>
Activate/deactivate nightly upgrade on an instance
sim autoupdate <name>
sim noautoupdate <name>
Activate/deactivate auto-save on an instance
sim autosave <name>
sim noautosave <name>
Set/reset custom URL of an instance
sim seturl <name> <custom URL>
sim reseturl <name>
Set version of an instance
sim setversion <name> <version>
Only a higher version than current instance version is possible. If set to lower version, the instance will not start anymore.
Set status of an instance
sim setstatus <name> <started|stopped>
The status is set by start/stop actions, use this only if there was an unexpected issue and the status is incorrect vs actual instance's status.
Get health check of an instance
Only to get a return code:
sim health|healthcheck <name>
Or get full health check data:
sim status <name>
Or simple ping status:
sim ping <name>
Show process of an instance
sim ps <name>
Start shell for instance
sim shell|sh <name>
Connect to instance's database
sim database|db <name> [<input file>]
The client tool used to connect to database depends on the database vendor (e.g. mysql client is used for MySQL/MariaDB, psql for PostgreSQL, ...)
With embedded HSQLDB the instance must be stopped before connecting to database.
Instance monitoring
sim monitor <name> [<interval in seconds, defaults to 60>]
Monitoring is done by calling instance's /health endpoint. Each time a monitoring error/warning is detected
a call to the optional hook monitoring.sh is done with a reason argument.
Run a unit tests shared code on an instance
sim unitttests <name> <unit test shared code name>
SonarQube analysis for instance's module(s)
sim sonar <name> [<module 1> [<modules 2> ...]]
If no module is specified all modules are analysed.
A SonarQube server must be installed and configured.
Advanced CLI usage examples
This example gets status of all instances of a given version:
for NAME in `sim ls 5 | awk '{print $1}'`; do sim health $NAME | grep status; done
This example stops all instances with matching names:
sim ls myinstances* | awk '{print $1}' | xargs -L 1 sim stop
This more advanced example upgrades all started instances of version 4.0 or 5 that needs upgrade:
sim list "SQL:i.version in ('4.0', '5') and i.status = 'started' and i.version_date < v.date" | awk '{print $1}' | xargs -L 1 sim upgrade
Etc.
Hooks
It is possible to extend the manager behavior using the following script hooks (located in <manager home>/hooks):
pre-add.sh
post-add.sh
pre-reset.sh
post-reset.sh
pre-upgrade.sh
post-upgrade.sh
pre-save.sh
post-save.sh
pre-start.sh
post-start.sh
pre-stop.sh
post-stop.sh
pre-del.sh
post-del.sh
monitoring.sh
All hooks receive as argument their caller script's arguments (e.g. instance name, version and options for pre/post-add.sh).
If your usage of the hooks is to add/alter elements to instances' Tomcat (configuration files, additional Java JARs or static web components, ...)
you need to do it in the pre/post-add.sh but also in the pre/post-upgrade.sh (and maybe also in the pre/post-reset.sh) as upgrade (and reset)
actions reinstall Tomcat.
Examples
This post-start.sh hook looks for a license XML key named license-<instance-name>.xml
in the licensekeys folder located in the base $APPS_HOME folder,
if present this file is loaded on the instance's I/O endpoint using the appropriate credentials
(which are available as environment variables):
#!/bin/bash
XML=$APPS_HOME/licensekeys/license-$USER.xml
if [ -f $XML ]
then
echo "Importing $XML file..."
RES=`curl -s -u $SERVICE_USER:$SERVICE_PASSWORD --form service=xmlimport --form file=@$XML $SERVICE_URL`
if [ "$RES" = "OK" ]
then
mv -f $XML $XML.`date +%Y%m%d%H%M%S`
echo "Done"
else
echo "Failed to import $XML: $RES"
fi
else
echo "No $XML file"
fi
This license key example can easily be transposed to any data import on the I/O endpoint.
Configuration
Global settings
The global settings are set as environment variables in the <manager home>/config.sh file.
Core settings
Manager settings
APPS_BASEURL(mandatory) manager base URL, e.g.mymanager.simplicite.ioAPPS_USERNAME(optional) manager username (defaults tosimplicite)APPS_PASSWORD(optional but highly recommended), manager password (defaults tosimplicite)APPS_ROOTCONTEXT(optional) deploy instances as root contexttrue/false(defaults totrue)APPS_DEFAULTVERSION(optional) default Simplicité versionAPPS_DATABASES(optional) managed database types (comma-separated list ofhsqldb,mysql,postgresql,oracleandmssql(defaults tohsqldb,mysql,postgres)APPS_DEFAULTDATABASE(optional) default database type (one of above list items, defaults tohsqldb)APPS_MAXINSTANCESmaximum number of instances,0means no limit (defaults to0)APPS_ALLOWDOWNLOAD(optional) allow download of instances (yes/no, defaults toyes)APPS_DEFAULTPROTECTED(optional) create instances protected by default? (yes/no, defaults tono)APPS_DEFAULTAUTOSAVE(optional) create instances auto-saved by default? (yes/no, defaults tono)APPS_DEFAULTAUTOUPDATE(optional) create instances auto-updated by default? (yes/no, defaults toyes)APPS_GOOGLE_API_KEY(optional) Google API key to use on instances (defaults tonone)APPS_REALMNAME(optional), authentication realm name (defaults toSimplicite Instance Manager)APPS_EMAIL(optional), support email address (defaults tosupport@simplicite.io)
System settings
These system settings SHOULD NOT be changed unless you know precisely what you are doing.
APPS_USERLinux user used by the manager (defaults tosimplicite)APPS_GROUPLinux group used by the manager (defaults tosimplicite)APPS_HOMEHome directory in which the manager is located (defaults to/var/simplicite)
SSL settings
APPS_SSL(optional) use SSL ? 'true/false/force(defaults totrue`)APPS_SERVER_CERT(mandatory if use SSL =true) server certificate (stored in/etc/ssl)APPS_SERVER_KEY(mandatory if use SSL =true) server certificate's key (stored in/etc/ssl)APPS_SERVER_CA_CERT(optional) CA certificate to use for server (stored in/etc/ssl)APPS_CLIENT_CA_CERT(optional) CA certificate to use for client authentication on manager UI & API (stored in/etc/ssl)APPS_CLIENT_CA_PATH(optional) path of CA certificate to use for above client authentication check
Backup settings
APPS_SAVE_DIRcustom location for local directory used by manual save actions (defaults to$APPS_HOME/save, MUST be changed if the size of the$APPS_HOMEis not adapted for the volumes of the backup files)APPS_SAVE_DIR_DEPTHdepth (in days) of local save directory files (defaults to0which means no limit, minimum value is1)APPS_SAVEALL_DIRcustom location for local directory used by automatic save action (defaults to$APPS_SAVE_DIR)APPS_SAVEALL_REMOVE_LOCAL(optional) remove local automatic save files after transfer?true/false(defaults tofalse)
The following parameters only applies to the upgrade action (manual or automatic):
APPS_SAVEBEFOREUPGRADEdo an automatic save action before any upgradeAPPS_BACKUPBEFOREUPGRADEdo a backup before any upgrade = copies thetomcatdirectory of the instance astomcat.upgrade.bak
SCP destination
APPS_SCP_SERVER(optional) server to copy backups to using SCP protocol (with private/public SSH keys)APPS_SCP_USER(optional) user for SCP serverAPPS_SCP_PATH(optional) path on SCP server
FTP destination
APPS_FTP_SERVER(optional) server to copy backups to using FTP protocolAPPS_FTP_USER(optional) user for FTP serverAPPS_FTP_PASSWORD(optional) user for FTP serverAPPS_FTP_PATH(optional) path on FTP server
OpenStack object storage container destination
APPS_OS_CONTAINER(optional) main URL of the OpenStack container to copy backups to using HTTP protocolAPPS_OS_PREFIX(optional) prefix to prepend to the name of stored files in the main containerAPPS_OS_CONTAINER_ALT(optional) secondary URL of the OpenStack container to copy backups to using HTTP protocolAPPS_OS_PREFIX_ALT(optional) prefix to prepend to the name of stored files in the secondary containerAPPS_OS_AUTH_URL(optional) OpenStack authentication URLAPPS_OS_TENANT_NAME(optional) OpenStack tenantAPPS_OS_USERNAME(optional) OpenStack userAPPS_OS_PASSWORD(optional) OpenStack password
Google Cloud object storage bucket destination
APPS_GS_BUCKET(optional) name of the Google Cloud storage bucket to copy backups to using thegsutiltool (which needs to be configured manually)
AWS S3 object storage bucket destination
APPS_S3_BUCKET(optional) name of the AWS S3 storage bucket to copy backups to using theaws s3tool (which needs to be configured manually)
E-mail settings
APPS_MAILSERVER(optional) mail server IP address or host name (no default)APPS_MAILPORT(optional) mail server port (no default)APPS_MAILUSER(optional) mail service username (no default)APPS_MAILPASSWORD(optional) mail service password (no default)
SonarQube settings
APPS_SONARURL(optional) SonarQube server URL (defaults tohttps://sonarqube.io)APPS_SONARLOGIN(optional) login or security token to connect to SonarQube server (no default)APPS_SONARPASSWORD(optional) password to connect to SonarQube server, not required if the above is a security token (no default)APPS_SONARORG(optional) organization name, not applicable to SonarQube community edition (no default)
Databases settings
MySQL settings
APPS_MYSQL_HOST(optional) database server IP address or hostname (defaults tolocalhost)APPS_MYSQL_PORT(optional) database server port (defaults to3306)APPS_MYSQL_ADMINUSER(optional) database administrator user (defaults toroot)APPS_MYSQL_ADMINPASSWORD(optional) database administrator password (defaults to empty string)
PostgreSQL settings
APPS_POSTGRESQL_HOST(optional) database server IP address or hostname (defaults tolocalhost)APPS_POSTGRESQL_PORT(optional) database server port (defaults to5432)APPS_POSTGRESQL_ADMINUSER(optional) database administrator user (defaults topostgres)APPS_POSTGRESQL_ADMINPASSWORD(optional) database administrator password (defaults topostgres)
Oracle settings
APPS_ORACLE_HOST(optional) database server IP address or hostname (defaults tolocalhost)APPS_ORACLE_PORT(optional) database server port (defaults to1521)APPS_ORACLE_ADMINUSER(optional) database administrator user (defaults tosys)APPS_ORACLE_ADMINPASSWORD(optional) database administrator password (defaults tomanager)
Note that other Oracle-related environment variable can be set here if not set otherwise, e.g:
ORACLE_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/xe
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${ORACLE_HOME}/lib:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}
SQLPATH=${ORACLE_HOME}/lib:${SQLPATH}
PATH=${ORACLE_HOME}/bin:${PATH}
NLS_LANG=AMERICAN_AMERICA.UTF8
ORACLE_SID=XE
SQLServer settings
APPS_MSSQL_HOST(optional) database server IP address or hostname (defaults tolocalhost)APPS_MSSQL_PORT(optional) database server port (defaults to1433)APPS_MSSQL_ADMINUSER(optional) database administrator user (defaults toSA)APPS_MSSQL_ADMINPASSWORD(optional) database administrator password (defaults to empty string)
Note that other SQLServer-related environment variable can be set here if not set otherwise:
MSSQL_HOME=/opt/mssql-tools
PATH=${MSSQL_HOME}/bin:${PATH}
Version-level settings
The version-level settings are set as environment variables in the <manager home>/version-<version>.sh file (without the export keyword)
JVM settings
APPS_JDK(mandatory) JDK to use (must point to a JDK root folder such as/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0)APPS_ENCODING(mandatory) encoding to use with considered version (should beUTF-8unless your version's template is specifically packaged for another encoding)APPS_TOMCATMINMEM(optional) minimum JVM memory in Mb (defaults to128)APPS_TOMCATMAXMEM(optional) maximum JVM memory in Mb (defaults to512)
Auto-patching at instance startup
APPS_AUTOUPGRADE(optional) use built-in system patches application at instance's startup instead of legacy patches import (defaults totruefor versions 4.0 and more recent and tofalsefor versions lower than 4.0)
This feature is different from the fact that the instance is marked as nightly updated.
This APPS_AUTOUPGRADE setting just refers to the way an instance is being updated by the SIM:
false= legacy mode = the SIM updates the webapp and imports the patches through the I/O interface of the instancetrue= auto-patching mode = the SIM only updates the webapp and the patches are applied by the instance itself at startup
Instance-level settings
The instance-level settings are set as environment variables in the <instance home>/.simplicite file.
These variables are set upon creation of the instance based on the global configuration. In general they should not be changed manually unless you know what you are doing.
Example:
SERVICE_CONTEXT=
SERVICE_TOMCATMINMEM=256
SERVICE_TOMCATMAXMEM=1024
SERVICE_URL=http://localhost:10078/io
SERVICE_USER=designer
SERVICE_PASSWORD=d98990faa918c84584ef
SERVICE_DATABASE=oracle
SERVICE_DATABASE_HOST=localhost
SERVICE_DATABASE_PORT=1521
SERVICE_ORACLE_SID=XE
SERVICE_AUTOUPGRADE=true
SERVICE_DEBUG=false
SERVICE_DEBUG_ORIGIN=192.168.0.0
SonarQube
You can add the following variables for instance-specific SonarQube analysis settings:
SERVICE_SONARPROJECTto override the default project name/key prefix for the analysed modules (defauts to<base URL>-<instance name>). Note that the module name is appended to this as-<module name>in all cases.SERVICE_SONARURLURL of SonarQube server URL (defaults to$APPS_SONARURL)SERVICE_SONARLOGINURL of SonarQube login (defaults to$APPS_SONARLOGIN)SERVICE_SONARPASSWORDURL of SonarQube password (defaults to$APPS_SONARPASWORD)SERVICE_SONARORGURL of SonarQube server (defaults to$APPS_SONARORG)
Git credentials
If you are not using SSH keys and SSH URIs for your remote Git repositories, you can set the username and a password of your remote using:
SERVICE_REMOTE_GIT_USERNAMEremote Git usernameSERVICE_REMOTE_GIT_PASSWORDremote Git password
Note that you can also define a username and a password in each configuration of your modules, these global variables are only used as fallback if no explicit username and password are defined.