Web Page
What is a Web Page?
A Web Page in Simplicité, is a type of External Object that aims to be rendered as an interactive standalone page. Thus it is free of any peculiar interface constraints, and is supposed to be accessible to any user.
The specificity (which differentiates it from a Static Web Site) is that such object is allowed and meant to interact with Simplicité's backend.
External objects of this type are exclusively rendered in the public zone, which means they can't be embedded within Simplicité's
interfaces and are thus meant to be rendered at https://<your-instance-name>/ext/<object-name>, by default accessible to any user.
How to create
The creation process is similar to the one for any External Object:
-
Go to User Interface > External Objects > Show all, and then click Create
-
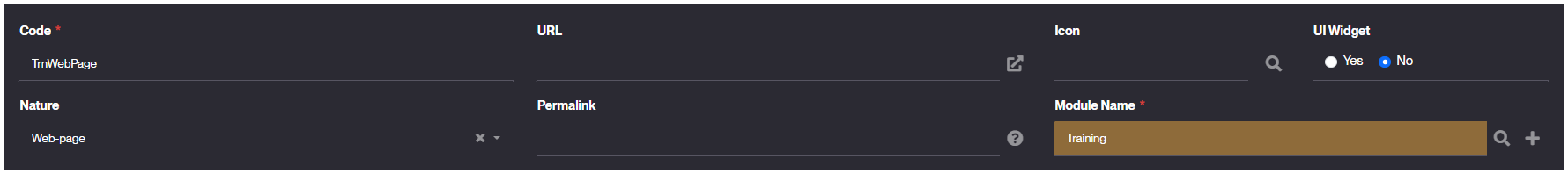
During the form's filling, ensure you select Web Page as Nature.
- UI Widget should be set as No
- Ensure you assign the right Module Name for your object.
Example values:
-
Click Save.
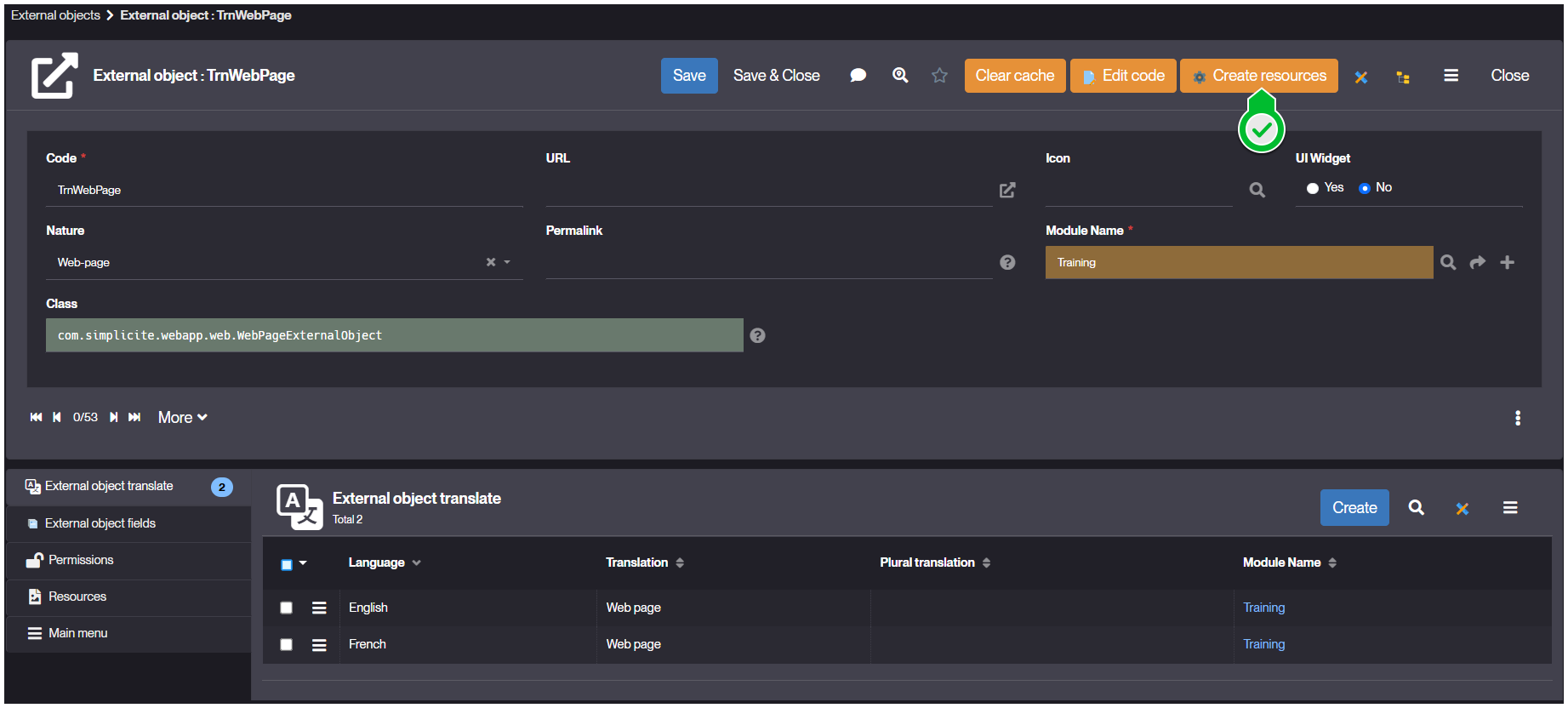
-
From the updated object's form, click Create Resources to create the web Resources.
- Ensure CLASS HTML and STYLES well appear in the Resources tab.
Created Resources:
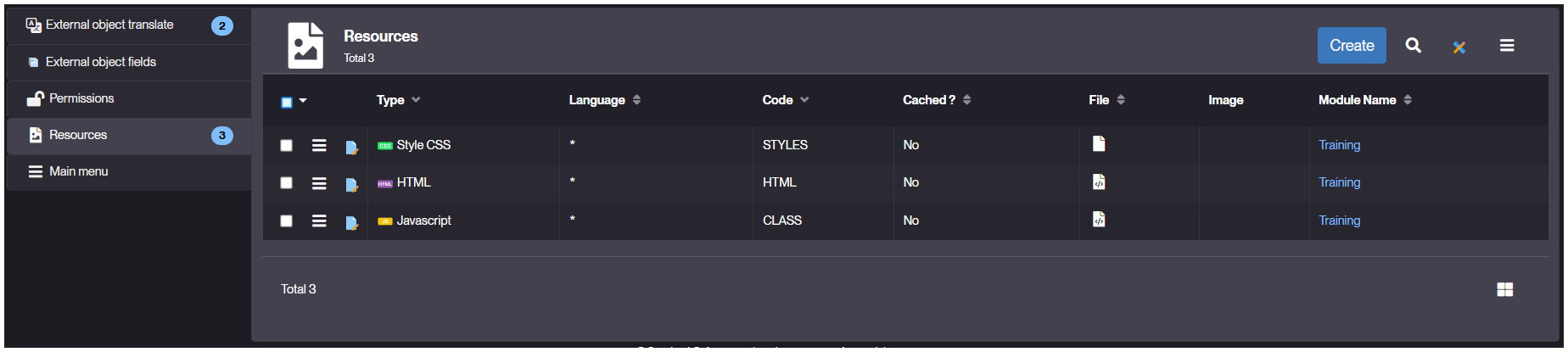
- Ensure CLASS HTML and STYLES well appear in the Resources tab.
-
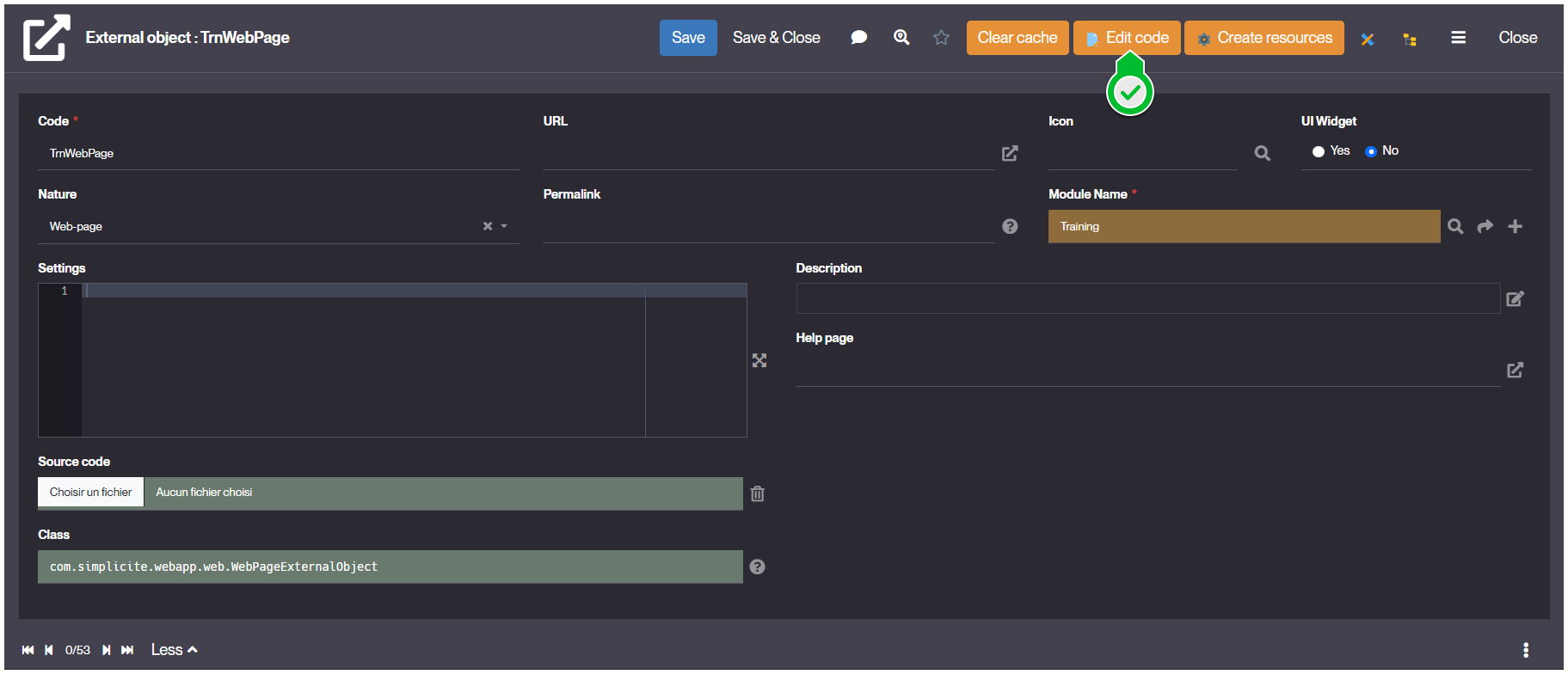
Finally, click Edit Code to create the custom Java class code for your object.
- You should see the Class field empty.
- Source Code field should have the
<your-object-code>.javafile referenced.Result Form:
The code for your webpage shall look like this by default:
package com.simplicite.extobjects._; // replace _ with <module-name>
import java.util.*;
import com.simplicite.util.*;
import com.simplicite.util.exceptions.*;
import com.simplicite.util.tools.*;
/**
* Standalone basic web page external object _
*/
public class _ extends com.simplicite.webapp.web.WebPageExternalObject { // replace _ with <object-code>
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* Body part of the page
* @param params Request parameters
*/
@Override
public String displayBody(Parameters params) {
try {
// Call the render JavaScript function implemented in the SCRIPT resource
return javascript(getName() + ".render();");
}
catch (Exception e) {
AppLog.error(null, e, getGrant());
return e.getMessage();
}
}
}
Usage
Using Web Page external objects, you have two logics to implement:
-
Client-Side logic: using the created web-resources, implement your object as you would for any native web-page.
- HTML: holds the content of your page, embedded in a
<div id="bs-main" class="container">...</div>, and accessible from scripts byconst $content = this.ctn;. - STYLES: where you define the stylesheet declaring all styles for your component. Using either CSS or LESS syntax.
- CLASS: the javascript file where you declare all of your component's behavior and interactions, within the
async render(){ ... }method. Which you can refine or extend by using server-side logic by callingthis. server()that references a custom method in the Java Code.
- HTML: holds the content of your page, embedded in a
-
Server-Side logic: here is defined your object's instantiation and global setup, in a class extending
com.simplicite.webapp.web.WebPageExternalObject.- Most of it is declared within the
public Object displayBody(Parameters params){ ... }. - Your page is rendered by referencing the CLASS resource through
javascript(getName() + ".render();"); - Other Possible Structure
- Your page is implemented using the
com.simplicite.webapp.web.BootstrapWebPageclass withnew BootstrapWebPage(params.getRoot(), getDisplay()). - Your CLASS javascript code is called using
String render = getName() + ".render(params.toJsonObject().toString())"thenwp.setReady(render)andreturn wp.toString(). - You can pass other types of resources to your client-side scripts by putting them into the
paramsvariable that you pass toString renderas follows;params.toJSONObject().put("<usableName>", HTMLTool.getResourceImageUrl(this, "<resource-name>")). - It's also here that you load your web-resources using the BootstrapWebPage embedded methods:
- CLASS with
BootstrapWebPage.appendJSInclude(HTMLTool.getResourceJSURL(this, "CLASS")) - STYLES with
BootstrapWebPage.appendCSSInclude(HTMLTool.getResourceCSSURL(this, "STYLES")) - HTML with
BootstrapWebPage.append(HTMLTool.getResourceHTMLContent(this, "HTML")).
- CLASS with
- Your page is implemented using the
- Most of it is declared within the
Code Example
@Override
public Object display(Parameters params) {
// Bootstrap page
BootstrapWebPage wp = new BootstrapWebPage(params.getRoot(), getDisplay());
wp.appendAjax(true);
wp.appendJSInclude(HTMLTool.getResourceJSURL(this, "CLASS"));
wp.appendCSSInclude(HTMLTool.getResourceCSSURL(this, "STYLES"));
wp.appendHTML(HTMLTool.getResourceHTMLContent(this, "HTML"));
JSONObject p = params.toJSONObject();
String imageResource = HTMLTool.getResourceImageURL(this, "IMAGE");
p.put("customImage", imageResource); // Add IMAGE image to params
wp.setReady(this.getName() + ".render(" + p.toString() + ");");
return wp.toString();
}
Read More
JavaDoc links:
Other documentation:
JS Dev: